Rosacea is a skin condition that primarily affects the face. Redness, dilated blood vessels, small red bumps, pustules, and skin sensitivity characterise rosacea. You’re not alone-it’s a common condition that affects individuals in the 30-50 age group and is commonly seen in people with fair skin. It is a chronic and inflammatory condition.
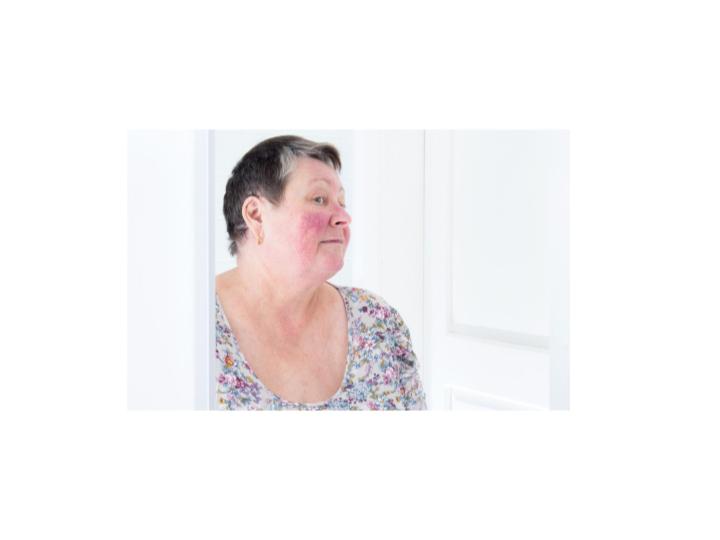
Types of Rosacea
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea:
In this type, facial redness is present, the skin appears flushed, and small blood vessels are visible on the skin’s surface. The symptoms are triggered by exposure to the sun, spicy foods, and stress, among others.
Phymatous Rosacea:
In this type, the skin exhibits a thickened texture with bumps, typically in the facial region. The skin of the face develops uneven skin texture.
Papulopsutular Rosacea:
This type includes inflammatory lesions with redness. It typically affects the cheeks, chin, and forehead. It is more common in middle-aged women. In some cases, the skin becomes oily and swollen.
Ocular Rosacea:
Ocular rosacea, as the name implies, mainly affects the eyes and eyelids, causing a variety of symptoms, such as redness and watery eyes. This type occurs before or alongside rosacea on the face.
Causes and Risk Factors of Rosacea
- Family history: Rosacea often runs in families.
- An abnormal response by the immune system causes rosacea
- Demodex mite is a natural skin mite that is more prevalent in people with rosacea.
- Helicobacter pylori bacteria stimulate the inflammation that affects the blood.
- Hot drinks, alcohol consumption, sun exposure, and mental stress can trigger this condition.
- Symptoms of Rosacea
- Persistent facial redness
- Blushing and flushing of the skin
- Small red bumps or pus-filled lesions appear on the face
- Burning sensation of the skin
- Visible blood vessels on the skin
- Thickened skin, especially around the nose.
- Dry, irritated and watery eyes.
- Sensitivity to skin care products.
Diagnosis of Rosacea
- Diagnosis is based on medical symptoms and physical examination.
- Ophthalmologic examination
- Blood tests
- Treatment of Rosacea
- Ointments
- Oral Medications
- Intravenous medications
Diet and lifestyle for Rosacea
- Understand and avoid personal triggers like spicy food, hot beverages, etc
- Avoid harsh skincare products
- Eat a balanced diet
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation and breathing exercises.
- Stay well hydrated by drinking 7-8 glasses of water per day.
- Get adequate sleep.
Consult a skin specialist if you notice persistent facial redness, flushed skin, bumps, or skin sensitivity. Remember, early diagnosis and trigger management can prevent flare-ups, improve skin health, and reduce the risk of permanent changes.
