Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition characterised by the presence of scaly eruptions on the body. Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can last for long periods. The eruptions cause inflammation, itching, and redness. Psoriasis is most commonly seen in adults; however, it can occur at any age. The condition can affect the whole skin and scalp. Psoriasis is not a contagious condition; it does not transfer from one person to another via contact. However, psoriasis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
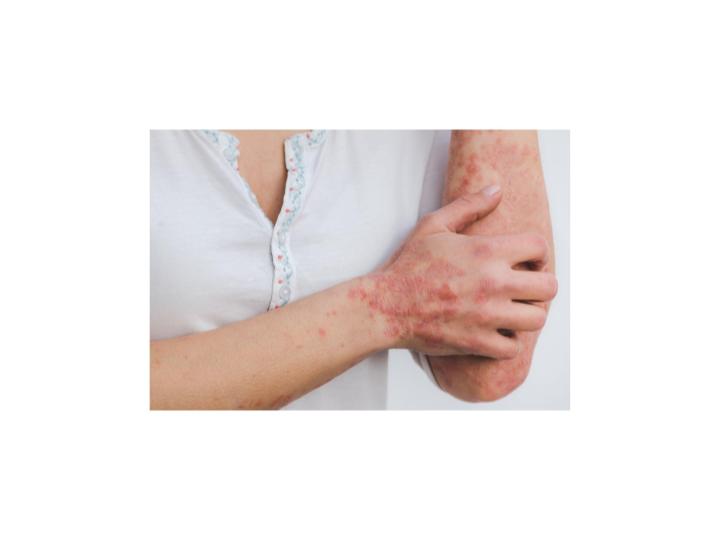
There are various types of psoriasis.
Let’s explore the various types of Psoriasis.
Plaque Psoriasis
This is the most common type of psoriasis. In this type, the eruptions are present on the skin; they are inflamed, itchy, and covered with silvery-white scales. It affects the elbow, knees, scalp and lower back.
Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is characterised by blisters or pustules filled with pus. This pus is non-infectious. This eruption first appears in one part of the body and gradually spreads to other parts.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis typically occurs in childhood, presenting as small, red, drop-shaped spots, and is often triggered by infections such as strep throat.
Inverse Psoriasis
It affects the skin folds, such as those under the breasts, in the armpits, and the groin region. This type of eruption shows shiny paths.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
A rare but severe form of psoriasis that leads to widespread itching, pain, and redness of the skin. This type of psoriasis requires prompt, immediate medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors of Psoriasis
- Family History and genetic predisposition.
- A dysfunctional immune system causes psoriasis because the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin in the body.
- Infections, such as streptococcal throat infections, can trigger guttate psoriasis.
- Mental stress can be a reason behind the psoriasis
- Medications like antimalarial drugs can trigger psoriasis.
- Cuts and sunburn can lead to the development of psoriatic patches
- Smoking and alcohol consumption can worsen the psoriasis
- Obesity increases the risk of psoriasis
Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Red paths of skin covered with thick and silvery scales.
- Dry itchy skin
- Skin bleeds on scraping
- Thickened and ridged nails.
- Stiff and swollen joints
- Periodic flare-ups followed by remission of symptoms.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
- Done based on detailed medical history and Physical examination
- Blood tests to rule out underlying diseases
- In some cases, a Skin Biopsy is done.
Treatment of Psoriasis
- Ointment
- Oral Medications
- Phototherapy
- Intravenous Medications
Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Psoriasis
- Eat food rich in antioxidants, including fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco consumption.
- Get adequate sunlight exposure, and stay hydrated by drinking sufficient water.
- Follow a consistent skincare routine and avoid harsh soaps.
Psoriasis can spread very quickly; hence, early diagnosis and treatment can help individuals recover more quickly. Psoriasis can lead to social anxiety or stress due to embarrassment. Professional help and counselling play an essential role in the healing process of the skin.
